The method of in vitro fertilization (IVF, artificial insemination) ) - is a process in which the husband’s sperm is «combined» with the wife’s oocyte outside their organisms, in the laboratory, using special media and laboratory glassware. One or more fertilized oocyte (embryos) are transferred to the uterine cavity, where they are attached to its uterine sidewall. Excess embryos can be frozen and used in another cycle. Initially, IVF was used to treat women with damaged, blocked or missing fallopian tubes, today the indications for use have expanded significantly and included endometriosis, ovulation disorder, male factor and infertility of unknown etiology.
Stages of in vitro fertilization
- ovarian stimulation;
- ovarian puncture;
- fertilization;
- cultivation (cultivation) of embryos;
- embryo transfer.
Stimulation of ovulation
When stimulating ovulation or inducing ovulation, drugs that stimulate the maturation of a large number of follicles are used, instead of one that normally grows in an unstimulated (natural) cycle. The main goal of stimulating ovulation is to grow many follicles, since part of the cell will not fertilize or will develop poorly after fertilization. Among the drugs used for this are recombined gonadotropin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, clomiphene; as well as drugs that prevent premature ovulation of GnRH antagonists. Some medicines are released in tablets, while others are given as injections. Tableted preparations have significantly less potency, so they are rarely used to stimulate ovulation. According to the literature, there is no evidence that one injection is better than another.
Follicular maturation is monitored by ultrasound of the ovaries while the number, size and structure are recorded.
Photo 1. Usually, stimulation lasts from 8 to 14 days. When the follicles have matured then the doctor prescribes chorionic gonadotropin, a drug that replaces the action of LH (luteinizing hormone) and helps the oocyte to get out of the follicle. Ovarian puncture is performed 34 to 36 hours after the administration of gonadotropin. Up to 20% of stimulation cycles can be terminated at any stage of stimulation, among the common causes, this is caused by this: a small number of follicles developing a poor ovarian response to drugs, especially after 35 years. If this happens, your doctor will prescribe other drugs that may be more effective.
Photo 1. A series of ultrasound images of the ovaries with stimulated follicles that look like large dark cavities.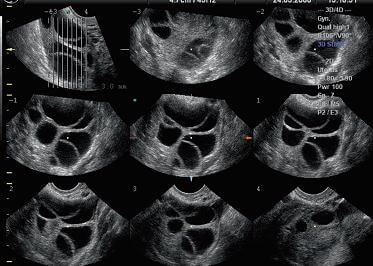
Ovarian puncture
Ovarian puncture is performed 34 to 36 hours after the administration of gonadotropin under the supervision of ultrasound and general anesthesia. The doctor punctures the follicle through the wall of the vagina using a special needle, connected to a vacuum pump. All fluid from the follicle, along with the oocytes are immediately transferred to the laboratory. The whole procedure lasts from 10 to 30 minutes. Some women experience a slight pulling pain in the lower abdomen in day of puncture or one day later, a feeling of fullness or pressure due to the large size of the follicles. The pain goes away in a few days.
Fertilization and cultivation of embryos
After the puncture, all the material goes to the laboratory, where the degree of maturation and the quality of the oocytes are determined. Ovums (photo 2) are placed in a special environment and stored in an incubator until fertilization. At the same time, the partner’s sperm is prepared in the laboratory, which he passes through masturbation. Sometimes, when there is no spermatozoon in the partner’s sperm, a testicle or an epididymis is punctured to obtain sperm for fertilization. Sperm preparation takes place in two stages: the first is the separation of sperm from seminal fluid, dead and immobile sperm, and the second is an additional washing in the medium, which contributes to the process of fertilization. Further, when the spermatozoons are ready, two fertilization options are possible: insemination or in vitro fertilization (IVF) - a procedure in which spermatozoons are placed in oocyte and left with it for a while, or intracytoplasmic administration of the sperm (ISCI) (intracytoplasmicsperminjection (ICSI) when one spermatozoon is injected into the egg. The intracytoplasmic administration is recommended to be used for low-quality sperm of the partner, as well as in the absence of fertilization during insemination. The percentage of pregnancy with the use of ICSI is the same as with insemination.
Photo 2. View of ovum. The red arrow indicates the polar body, which is an indicator of cell maturity: 5px;" src="https://bogolybu.com.ua/files/files/foto%202.jpg" alt="" width="300" height="272" />
The day after fertilization, two pronuclei appear in the cell, one is formed by oocyte, and the other by spermatozoon. Photo 3. Usually from 65% to 75% of oocytes are fertilized. Although the percentage of fertilization may be lower if the quality of sperm or eggs is poor. The embryo continues its development and two days after the puncture, it has from two to four cells.
Photo 3. The fertilized oocyte. The red arrow indicates pronuclei.
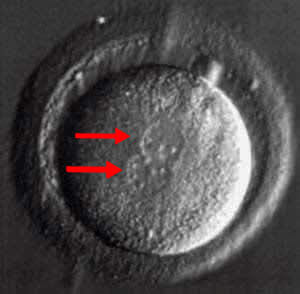
Photo 4. An embryo with two cells (blastomeres).
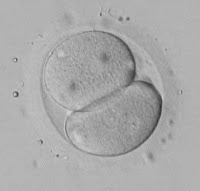
Photo 5. An embryo with four blastomeres. .
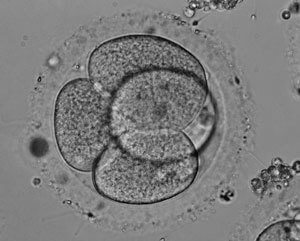
On the third day after fertilization, the cell contains from 6 to 10 blastomeres.
Photo 6.
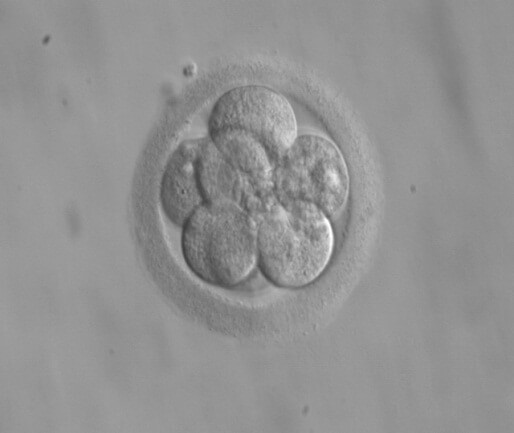
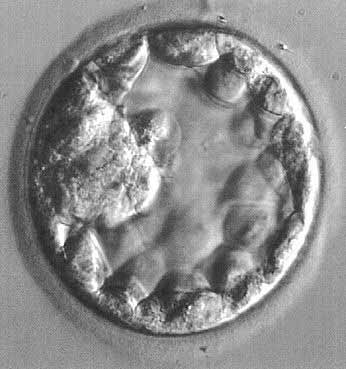
Photo 6. On the fifth day, a cavity forms in the embryo. At this stage of development, the embryo is called a blastocyst. Photo 7.
Photo 7. Blastocyst.
Embryos can be transferred to the uterine cavity at any stage of development. If embryo development continues in the uterus, then on 6-10 days after the puncture, it will be hatching and attach to its wall (implantation).
Assisted «hatching» Assisted hatching (AH) is a procedure in which a hole is made in the ovular membrane surrounding the egg to help the embryo to hatch. Today, it is not proven that such manipulation increases the likelihood of pregnancy. Hatching can be used for older women or women with unsuccessful previous attempts.
Embryo transfer
The next stage of in vitro fertilization is embryo transfer. This procedure is performed without pain medication. Using a survey mirror, the doctor finds the cervix. One or more embryos are collected into a catheter in a drop of medium. The doctor carefully moves the catheter through the cervix and releases the contents of the catheter into the uterus. Embryo transfer is a painless procedure, although some women experience mild pulling pain in the lower abdomen. The number of embryos depends on the age or other individual characteristics of the patient or embryo. Before the procedure, you can discuss with your doctor the number of embryos that will be transferred.
Cryopreservation
Embryos remaining after the procedure can be frozen for later use. The advantage of using frozen cells is that you do not need to stimulate and puncture the ovaries. Cryopreserved embryos can be stored for a very long time; there are known cases of the birth of healthy children after the 20th storage of embryos in a cryobank.
You need to know that not all embryos will survive after thawing, and the rate of pregnancy when using frozen cells is lower.
СThere are two methods for freezing cells: «slow freezing» and vitrification (ultra-fast freezing). The choice of method depends on the experience of the clinic staff. Although there is evidence that vitrification gives better result.
When using frozen sperm, eggs or embryos, the birth rate of a child with defects or chromosomal abnormalities, pregnancy complications or transmission of infectious diseases is not higher than when using «fresh» sperm, eggs or embryos.
Program Success
Information on the results of various clinics should be interpreted with great care. The success rate of the in vitro fertilization program depends on many factors and comparing the work of different clinics is not objective, since approaches to treating patients differ in different clinics. You also need to understand the definition of the level of pregnancy (pregnancyrate) and the birth rate of live children (livebirthrates). For example, a 50% pregnancy rate does not mean that in 50% of cases you will give birth to a baby. Pregnancy does not always end with the birth of a baby. A biochemical pregnancy is a pregnancy that is confirmed by the results of a blood or urine test, but with ultrasound diagnosis it is not determined, since it stops before it is visible on an ultrasound scan. Clinical pregnancy is a pregnancy that is visible when using ultrasound. So, comparing the results of the programs of various clinics, you need to know what level of pregnancy and the birth rate of children, the latter is more interested in couples, as it reflects the level of ability to give birth to a started program of in vitro fertilization. These factors are influenced by many factors, especially the age of the woman.
Donor sperm, oocytes and embryos
In vitro fertilization can be done with your eggs and sperm, or donor cells. A couple can use donor material if their own eggs or sperm are of poor quality or there is a risk of transmitting genetic diseases to the child. The donor may be known or anonymous. In most cases, donor sperm is taken at Cryobank. Donors undergo a full physical examination and laboratory tests before using their cells. Donor sperm is frozen and placed in quarantine for three months in a cryogenic repository. After confirming the negative results of all laboratory tests, it can be used for intrauterine insemination or in vitro fertilization..
Donor eggs are used by women who cannot get pregnant when using their own eggs. Egg donors, like sperm donors, undergo almost the same examinations. Some donors receive compensation for participating in the program. Egg donation is a more complicated procedure than sperm donation, as egg donors must undergo a cycle of stimulation and ovarian puncture. At the same time, the cell recipient (a woman using donated eggs) is taking medications that prepare the uterus for implantation. After the puncture, donor eggs are fertilized with the partner's sperm and transferred to the uterus of the recipient. The recipient is not genetically related to the child, but is the biological mother who bore and gave birth to the child. Donor cell programs are expensive due to donor selection, screening and treatment, although they have a high birth rate.
In some cases, when a man and a woman are infertile, donor eggs and sperm can be used.
It is worth knowing that the decision to use donor material is not simple. It is recommended to have a conversation with a specialist who understands your needs and helps you make a decision. Also, consult with a representative of your interests about the possible legal aspects of using donor material.
Risks associated with the use of in vitro fertilization program
Risks that may arise during the program depend on the stage of the procedure.
Stimulation of ovarian function can take place against the background of hyperstimulation, when the ovaries become painful and tense. The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal or chest cavity can occur, accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. It is worth knowing that up to 30% of stimulation cycles can be accompanied by mild symptoms of hyperstimulation and dissapear when using pain medications. In approximately 2% of cases, hyperstimulation has an acute course and the following symptoms: rapid weight gain, fluid accumulation in the abdominal and thoracic cavities, impaired electrolyte metabolism, blood clotting, in rare cases, blood clots, kidney failure, or death. In such cases, patients are hospitalized until the end of the clinical symptoms.
Ovarian puncture may carry a slight risk of bleeding.
The level of development of multiple pregnancy exists if more than one embryo is transferred to the uterine cavity. There is also evidence that even with the development of one fetus, there is a slight chance that the birth will be premature and the baby will be born with a low weight. Bleeding in the first trimester can be a signal of a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy (the fetus is not implanted in the uterine cavity, but in the fallopian tube). If bleeding or pain occurs before 13 weeks, you should consult your doctor to determine it is reason. There is also evidence that early bleeding occurs more often in patients who have undergone in vitro fertilization and are not associated with a poor prognosis as in women who became pregnant in the natural cycle.
After IVF, possible miscarriages, even if the presence of the fetus is confirmed by ultrasound studies. About 15% of women under 35, 25% of 40-year-old women, 35% of 42-year-old women may have miscarriages after in vitro fertilization. Additionally, there is a 5% risk of ectopic pregnancy in IVF programs. There is no statistic data, in vitro fertilization is associated with an increase in the number of children who are born with malformations. Such studies are currently underway to establish the extent of this risk.
Assisted reproductive technologies require significant physical, financial, and emotional effort from patients. Many patients have an unreasonably high level of expectations regarding the in vitro fertilization procedure, although each program may fail. Patients may feel disappointed, irritated, or angry, resentful, and outraged. Sometimes, these feelings can lead to depression or a decrease in self-esteem, especially immediately after an unsuccessful attempt. The support of friends and family is very important at this time. Also, psychological assistance of a specialist is possible, as an additional means of overcoming stress.
Preparing for in vitro fertilization
Preparing for a program can be just as important as the program itself. Ovarian reserve testing is performed to predict follicular growth and development during stimulation. The chance of becoming pregnant can be very low if the research results show a reduced ovarian reserve of the ovaries. It can be determined using such tests: the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol on the second or third day of the menstrual cycle and counting follicles in the ovaries. If, for example, the level of FSH / estradiol is high and the number of follicles is low, then the pregnancy rate is lower than in women who have normal rates. Although the patient's age remains the main factor in determining the possibility of becoming pregnant.
Pathological changes in the uterus, such as nodes, polyps, membranes, must be removed before IVF. accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tube and blockade reduce the likelihood of pregnancy. Some doctors recommend removing a damaged tube or clipping it.
If pathological changes are found in the analysis of seminal fluid, it is recommended to consult with an andrologist-urologist to determine the cause of the changes. For example, genetic abnormalities in the Y chromosome of men may be associated with male infertility; men who are born with missing vasdeferens (a channel that transports sperm from the testicles) are often carriers of the gene for the disease of cystic fibrosis. In these cases, genetic counseling is needed.
Men who secrete sperm, but without spermatozoons in it, carry out the isolation of sperm from reproductive tissues. Among these procedures are: aspiration of sperm from the epididymis (micro epididymal spermaspiration (MESA), extraction of sperm from the testis (testicular spermextraction (TESE). The first is used to extract sperm from men after vasectomy (sterilization) or the absence of vasdeferens from the testis) carried out under local or general anesthesia in the absence of sperm in the semen.
Lifestyle modifications increase pregnancy rates. For example, smoking can reduce pregnancy rates by up to 50% as well as being overweight, which carries the risk of miscarriage. Therefore, weight loss with obesity and smoking cessation will improve the results of in vitro fertilization. Alcohol, caffeine, and other medications should be limited or discontinued.
Taking folic acid before in vitro fertilization reduces the risk of congenital malformations of the nervous system. A medical examination and a cytological examination of the secretions from the cervix allows you to identify pathological conditions that need to be corrected before pregnancy.
Cost of In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilization price is formed depending on many factors. It must be remembered that the cost of the initial consultation, screening tests, medications and the technique of intracytoplasmic sperm administration may not be included in the total cost of the program. Other costs that you should pay attention to are transportation and those associated with absence at work.
Choice of clinic
When you choose a clinic for in vitro fertilization the following information is important. Particular attention should be paid to the qualifications and experience of the staff, the category of patients served by the clinic, the availability of additional services, the cost of the program and the birth rate of children. It must be remembered that new clinics may not provide information on the birth rate of children, since they are at the stage of accumulating information, although the clinic staff has extensive experience. Each couple, chooses a clinic, wants to choose a successful program, although a lot of factors affect the results of work. For example, some clinics accept only those patients whose chances of having a healthy baby are very low, as a result, the birth rate of children is low, which is explained only by the category of patients, the clinic serves; or some institutions specialize in treating only rare pathologies or using certain methods, will automatically reduce the result of having children, although at the same time the clinic staff are recognized specialists in the field of medicine. Some couples choose a clinic with their personal impression of the staff, the location of the clinic and the cost of services.
When to End the In Vitro Fertilization Program
According to research, the chance of getting pregnant remains the same in four in vitro fertilization cycles. Although you need to take into account many other factors in order to decide on the end of in-vitro fertilization, including the cost of the program.