The term «thrombophlebitis» indicates a general inflammation of the venous wall associated with the formation of a blood clot inside.
The presence of a blood clot complicates blood flow in the lumen of the vessel and causes a slowdown in blood circulation. Thrombophlebitis can occur for various reasons. The pathological process mainly affects the veins of the lower extremities, however, it can also affect the vessels of the hands and neck. If inflammation is noted in the superficial veins, then we are talking about superficial (or simply thrombophlebitis), and with deep vein thrombophlebitis it is more correct to say that we are dealing with thrombosis.
If inflammation is noted in the superficial veins, then we are talking about superficial thrombophlebitis (or simply thrombophlebitis), and with deep vein thrombophlebitis it is more correct to say that we are dealing with thrombosis.
Symptoms of Thrombophlebitis
Signs of thrombophlebitis often include:
-pain along the vein;
- local edema;
- swelling of the face and limbs;
- redness of the skin.
A problematic section of a vein can be detected by clinical palpation (not always).
In rare cases, thrombophlebitis can cause very severe pain and immobility. Blocked veins may be affected by infection (septic thrombophlebitis).
Deep vein thrombophlebitis (thrombosis) is characterized by more serious symptoms: increased body temperature, fever, chills, the skin becomes bluish (cyanosis), movement becomes impossible due to pain.
Causes and risk factors for thrombophlebitis
A thrombus is «born» born
after the attachment of platelets to the walls of the vessel, which are usually smooth, but may have roughness and plaque, which contribute to thrombosis. The platelet mass gradually increases in size, occupying the lumen of the vessel and reducing its diameter. In some cases, a blood clot can break away from the vessel wall, and a blood clot enters the bloodstream. This situation is fraught with tissue ischemia and necrosis. The cause of thrombophlebitis can be a decrease in the speed of blood in the veins, for example, due to a prolonged stationary state. Venous congestion often occurs in bedridden patients (for any chronic illness, heart failure, stroke, trauma, or after surgery) and in people who maintain a sedentary position (air travel, long-distance travel).
Risk factors
Thrombophlebitis contributes to trauma to the venous endothelium by infection, intravenous catheters, injection needles or chemotherapeutic agents. Thrombophlebitis contributes to trauma to the venous endothelium by infection, intravenous catheters, injection needles or chemotherapeutic agents. Pregnancy and varicose veins are associated with a risk of superficial thrombophlebitis.
Pregnancy and varicose veins are associated with a risk of superficial thrombophlebitis. Some tumors can cause thrombosis. Other risk factors include:
- age over 60 years;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- the use of intravenous drugs.
Complications of thrombophlebitis include pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, stroke. Congestive pigmentation is often found, especially with repeated cases of thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis treatment .
Thrombophlebitis treatment.
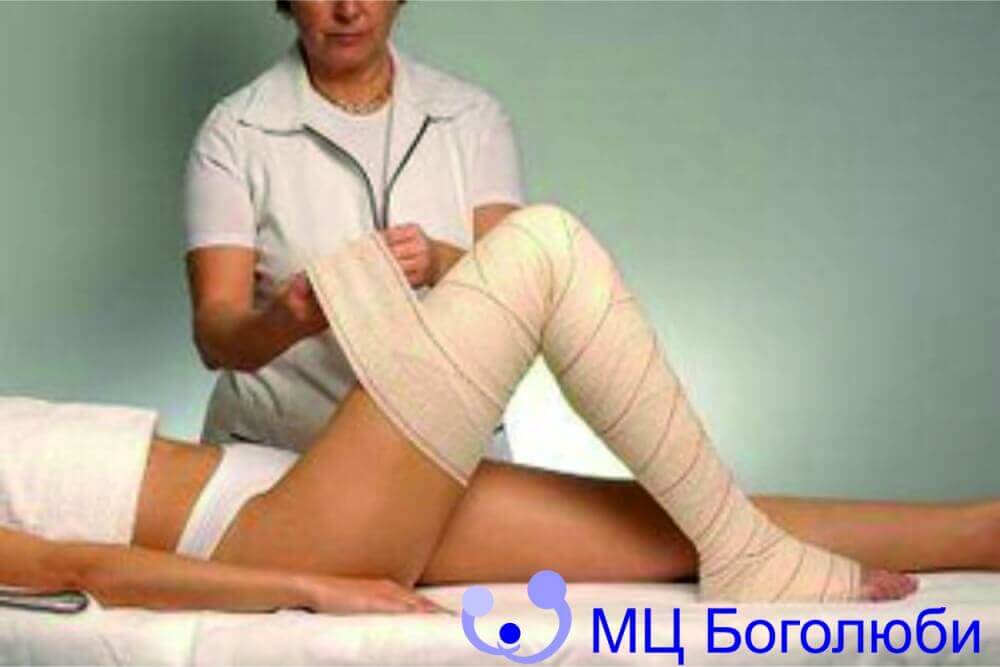
Thrombophlebitis is difficult to treat. The use of ointments (hesperidin, rutin), elastic support (stockings or bandages) may be recommended. In some cases, it is possible to use anticoagulants to reduce edema and the likelihood of thrombosis and embolism.