In our previous article, we spoke about such an important physiological cycle of a woman as ovulation. Today we will continue this topic, dwelling in more detail on the processes that occur in the female body after ovulation.
After ovulation, granulosa cells under the influence of luteinizing hormone accumulate yellow pigment and turn into cellula luteinica, which form the corpus luteum and secrete progesterone. This hormone, together with estrogens, determines the transition to the secretory phase in cyclic changes in the uterine mucosa, which is a preparation for implantation of the embryo. If fertilization does not take place, the corpus luteum becomes maximally developed approximately 9 days after ovulation. It can be easily recognized as a yellowish elevation above the surface of the ovary. Further, the corpus luteum decreases in size due to the degeneration of luteocytes and forms a mass of fibrous scar tissue, known as a whitish body. At the same time, progesterone production decreases accelerating menstrual bleeding. If the egg is fertilized, chorionic gonadotropin prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum. This hormone is produced by the trophoblast of the embryo, which develops. The corpus luteum continues to grow and forms the corpus luteum of pregnancy. By the end of the third month, this temporary formation can reach the size of a third or half of the whole ovary. Yellow luteocytes continue the secretion of progesterone until the end of the fourth month. After that, it regresses as the secretion of progesterone by the trophoblastic component of the placenta becomes sufficient to maintain pregnancy. Removing the corpus luteum during a fourth month usually leads to an abortion. Sperm that have just entered the female genital organs are not capable of fertilizing an egg.
To gain this ability, they must pass: :
A) capacitation;
B) acrosomal reaction;
Capacitation - is a period of chemical modification of the surface of sperm in the female genital organs. In humans, this process lasts approximately 7 hours. The main meaning of capacitation, which is carried out in the fallopian tube, is the interaction between the sperm and the surface of the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube. In this case, the glycoprotein coating and seminal fluid proteins are removed from the plasma membrane of the acrosomal site of the sperm. Only capacitated sperm can pass through the radiant crown of the oocyte and carry out an acrosome reaction.
Acrosomal reaction. The meaning of this reaction is to release the enzymes necessary for penetration of the transparent zone - acrosin and trypsin-like substances. Fertilization phases include: phase 1, penetration of the radial crown; phase 2, grinding of the transparent zone; phase 3, fusion of the membranes of the oocyte and sperm.
PHASE 1: Penetration of the radiant crown
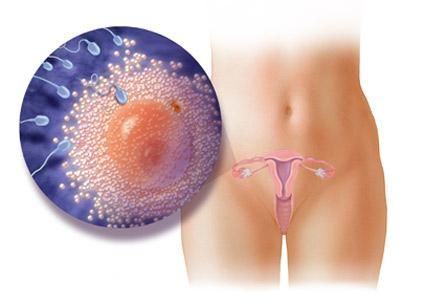
Of the 200-300 million sperm that enter the female genital organs during ejaculation, only 300-500 reach the place of fertilization. И только один из них оплодотворяет яйцеклетку. And only one of them fertilizes the egg. Capacitated sperm easily penetrate the cells of the radiant crown.
PHASE 2: Penetration of the transparent zone
The transparent zone is the glycoprotein membrane that surrounds the egg, it provides binding of spermatozoa, and also induces an acrosome reaction. The release of acrosomal enzymes (acrosin) allows the sperm to penetrate the transparent zone and come into contact with the plasma membrane of the oocyte. After the interaction of the sperm head with the oocyte surface, the permeability of the transparent zone changes. Many sperm can be immersed in the transparent zone, but only one of them will be able to penetrate the oocyte.
PHASE 3: Merging of the cell walls of the oocyte and sperm
Following adhesion, the plasma membranes of the sperm and egg are fused. In humans, the sperm head and tail enters the oocyte cytoplasm, while the sperm plasmalemma remains fixed to the surface of the egg.
The main results of fertilization:
- restoration of the diploid set of chromosomes, half of which comes from the father and half from the mother. Determination of the sex of a new individual.
- crushing initiation.
If fertilization has not occurred, the egg degenerates 24 hours after ovulation.