Atheroma is a benign neoplasm that develops as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. This pathology is found not only in adult patients, but also in children, and even - in infants. Speaking about atheroma, you should remind yourself that the sebaceous glands are a unique structural unit located on the entire surface of our body.
Atheroma Classification
Atheromas are classified according to location and characteristics of cystic contents. At the moment, the following types of atheromas have been sufficiently studied:
- reticular follicular cysts, they are usually called secondary atheromas, (a typical complication of acne);
- epidermoids are benign in nature, congenital formations that are located mainly in the areas of the presence of hair follicles.
The causes of atheromas are the following factors: metabolic disorders, inflammation of the hair follicles, congenital malformation of the sebaceous gland, hormonal dysfunction, illiterate use of cosmetics (especially decorative), violation of personal hygiene.
Symptoms
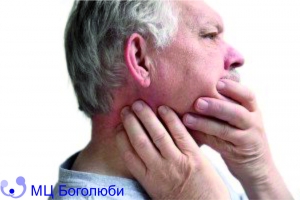
Since most neoplasms of the sebaceous glands do not show pronounced clinical signs, the only signal, a visual indicator that something is «wrong» is the detection of an atypical and dense formation on the body.
Characteristics of atheroma: elastic structure, clear contours, mobility of the subcutaneous capsule, slight swelling of the surrounding tissue. A more accurate initial diagnosis is made by a specialist during a physical examination.
Atheroma is not characterized by pain, the only drawback is a visible aesthetic defect. A tumor can cause discomfort if it forms in places where it comes in contact with clothing. In such cases, the skin on the atheroma is reddened, fluctuation is noted upon palpation.
Atheroma or lipoma?
A differential diagnosis is very important, since atheromas resemble lipomas in appearance.
Lipoma is a classic «wen», formed in adipose tissue, under the skin. By its consistency, it is much more plastic and softer than atheroma. «Favorite» places of lipomas are hips, shoulders, belly. A distinctive feature is the tendency to germinate to the deep dermal layers, down to muscle tissue. A lipoma grows extremely slowly, over the years, without showing anything of its presence.
General summary: lipomas are benign tumors that do not have cavities, and atheromas are, in fact, cysts, with their own capsules and contents. It is difficult to determine the diagnosis itself, it is much more reasonable to seek the help of specialists who are experienced in solving such issues.
Relapse of atheroma
Ateroma can recur only when the cystic capsule is not completely removed. The tumor should be completely removed, and if necessary even with adjacent tissues, especially if there is suppuration. Sometimes relapse of atheroma occurs when, for example, a dermoid cyst is taken for it, which is also removed surgically, but using other specific techniques.
ЧOften, recurrent atheromas are associated with hyperhidrosis, and cysts form in the adjacent channels of the sebaceous gland, and not in the postoperative place. Self-medication is also fraught with recurring atheroma.
Risks
Atheroma is not life threatening to the patient. A possible complication is suppuration. It should be understood that atheroma does not resolve, and it is believed that education can in any way squeeze out a self-dangerous delusion. Such practice can provoke a serious complication, for example, sepsis.
Treatment of atheroma
The only way to get rid of a tumor is its surgical removal. Atheroma can be operated on under local anesthesia with extrusion of the cyst. Small cysts are removed using laser technologies that are successfully used by surgeons of the Bogoliuby MC. The operation is not of significant complexity, cosmetic sutures are usually removed two weeks after the procedure.